
Typical investment portfolios diversify broadly, often via multiple index ETFs. There are two problems with this sort of over-diversification. The first is that it doesn't protect against systemic, or market risk. When the market crashes, as it did in 2008, nearly all stocks plummet, and most other asset classes decline as well (as gold did, for example).
The second problem is that high diversification dilutes potential returns. Instead of having your money concentrated in a handful of investments with the highest expected returns, you have it diluted among many investments with mediocre prospects.
Since each security is hedged, your potential downside is strictly and precisely limited, without the need for broad diversification or asset allocation. This means you can concentrate your assets in a handful of hedged securities with the highest expected returns.
Just enter the dollar value you are looking to invest, and the maximum drawdown you are willing to risk over the next six months (your "threshold")1. Portfolio Armor will present you with an optimally hedged and allocated portfolio with the highest expected return, given your risk tolerance.2
Every trading day, Portfolio Armor generates high-end estimates of how more than 4,000 stocks and exchange-traded products will perform over the next six months. These estimates are based on analysis of historical returns as well as option market sentiment, which provides a forward-looking element. We call this high-end estimate a security's potential return. Essentially, it's how the security might perform over the next six months in a bullish scenario. We backtested this method by running our analysis every trading day over an eleven-year period and then looking at the actual returns of the securities with the highest potential returns on our daily scans over the next six months. Over that 11-year period, we conducted 25,412 comparisons of our calculated potential returns to actual returns, an average of 9.4 top-ranked securities each trading day. The average potential return we calculated was 22.4%. The average actual return over the next six months, unhedged, was 6.84%. Since the average actual return was 0.3x the average potential return, we used that 0.3x multiple to derive expected returns from our potential returns. While a potential return represents a bullish upside, an expected return is the more likely result. In July of 2019, we began adding data from our top names generated since mid-2017 and tracked in real-time to our backtested data using a weighted average. We add new data every trading day and use it to refine our process. As of 2/24/2026, we now use a multiple of 0.2026 to derive expected returns from actual returns.
A subset of our top-ranked securities in our backtests had an even higher average actual return: 9.35%. All of our top-ranked securities were hedgeable with optimal collars, but the securities in this subset were also hedgeable with optimal puts (we call these AHP securities, for short). There aren’t always AHP securities available, but when there are, our portfolio construction algorithm gives preference to them proportional to their higher average returns in our tests. In our backtests, those returns were 3.23% higher than non-AHP returns, on average, over six months. In July of 2019, we began adding data from our top names generated since mid-2017 and tracked in real-time to our backtested data using a weighted average. We add new data every trading day and use it to refine our process. As of 2/24/2026, we now use a difference of 2.9122 to give preference to AHP names during our security selection process.
In June of 2022, we added an additional factor described here.
The security returns mentioned above were unhedged; we also tested gross returns (i.e., not net of hedging costs) of our security selection method while hedging against greater-than-9% declines. When doing so with optimal puts, the average gross return was 12.08% over six months. The average gross return for the same securities when hedged with optimal collars capped at their potential returns was about half as much, 6.25%, so the average gross return of securities hedged with puts was 1.93x that of securities hedged with collars, on average. This illustrates to what extent the average actual returns of the securities hedged with optimal puts were driven by outliers – securities that appreciated beyond our calculated potential returns. We adjust for the impact of potential outliers, and the difference in potential returns, during the portfolio construction process. As of July 2019, we updated the multiple we use to give preference to positions hedged with puts, after incorporating data from mid-2017 and later. As of 2/24/2026, we now use a multiple of 1.7591.
Next, Portfolio Armor uses its proprietary hedging algorithm to scan for an optimal collar hedge for each security, using the maximum drawdown you are willing to risk as the decline threshold, and each security’s potential return as the upside cap. The idea here is to capture each security’s potential return while minimizing your downside risk. At the same time, Portfolio Armor scans for uncapped optimal put hedges for each. In each case, where the security is hedged with an optimal collar and where it's hedged with an optimal put, we subtract the hedging cost from the security’s potential return to find the net potential return.
Because the average actual returns of securities hedged with puts are 1.7591 times higher than the actual returns of those hedged with collars, we assume that securities hedged with optimal puts will have a similarly higher net potential return than those hedged with optimal collars. If securities hedged both ways are available, Portfolio Armor will populate portfolios with the ones hedged with optimal puts, unless the ones hedged with optimal collars have net potential returns greater than 1.7591 the net potential returns of those hedged with optimal puts.
Portfolio Armor fine-tunes its selection based on the size of your portfolio in order to minimize costs. Where possible, it will use cash substitutes to minimize leftover cash and increase your portfolio's net expected return.3
Portfolio Armor's hedged portfolios can generate attractive returns during bull markets, and strictly limit your downside during sharp bear markets. Because our universe of more than 4,000 securities includes exchange-traded products such as inverse ETFs that can generate positive returns during long market declines, this can be used as an all-weather approach. During a long bear market, securities with the highest net potential returns may include bearish ETFs. Of course, you would be presented with optimal hedges for these, so if the market reversed direction while you held them, your downside risk would be strictly limited.
Consider the case of an investor with $1,000,000 to invest, who wants to maximize his expected return while limiting his downside risk over the next six months to a drawdown of no more than 20%. After clicking on the "Create Hedged Portfolio" tab in Portfolio Armor, he would be presented with the input screen below, where he would enter in the dollar amount he wants to invest ($1,000,000) and his "threshold", the largest decline he is willing to risk over the next six months (20%).
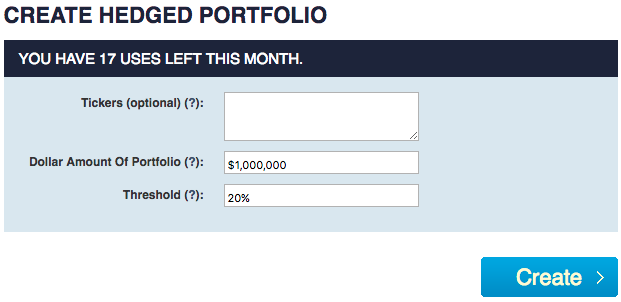
Had an investor done this at the close on June 22nd, 2017, after a few minutes of processing, he would have been presented with the hedged portfolio below.
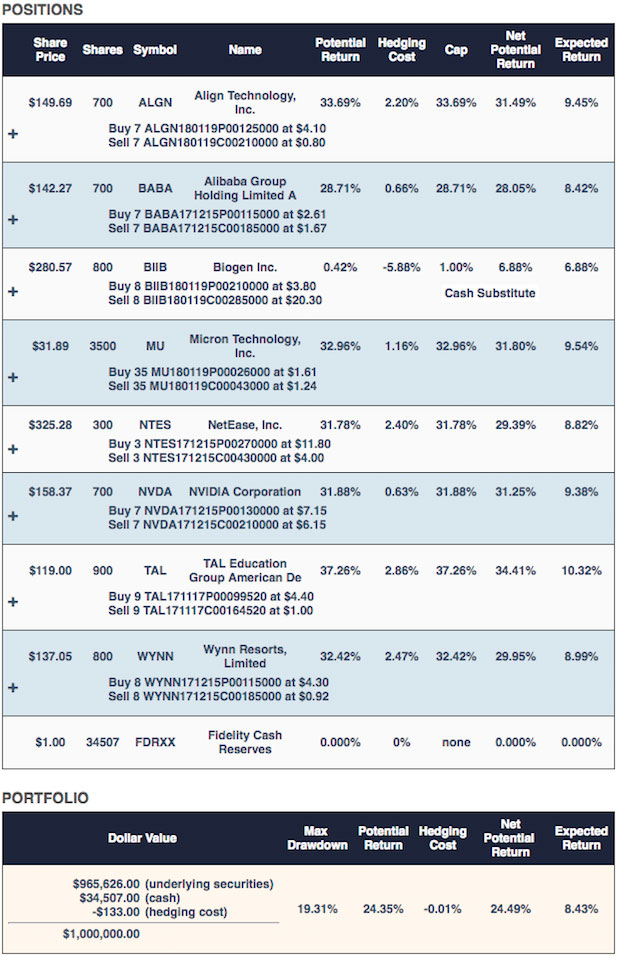
Note that, in the hedged portfolio above, each of the underlying securities is hedged with an optimal collar. In some other portfolios, some positions are hedged with optimal puts.
The maximum drawdown possible with this hedged portfolio was 19.31%: if every underlying security in this portfolio went to zero before its hedges expired, this portfolio would have declined by 19.31%. The hedging cost of this portfolio was slightly negative, meaning the investor would have collected a net credit of $133 when hedging these positions, assuming, conservatively, that he placed each hedging trade at the worst end of its respective spread. The net potential return of the portfolio was 24.49%, meaning that if every underlying security hit our bullish performance estimate over the next six months (an unlikely scenario), the portfolio would return 24.49% net of hedging costs and taking into account the cap on the cash substitute position. The expected return of the portfolio (which represented a more likely scenario), net of hedging costs, was 8.43%.
As it happened, this portfolio returned slightly more than 20%, as you can see in the chart below.
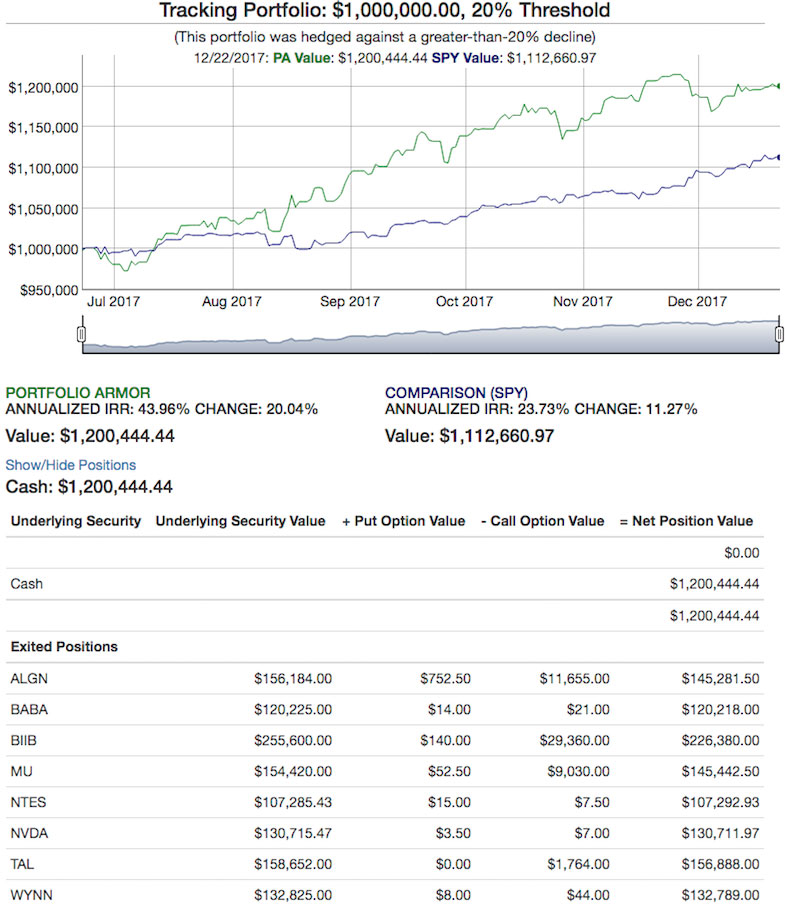
You can find more examples of portfolios like the one above created since mid-2017 and tracked in real time here. You can find sample backtests from 2003 to 2014 here.